Smartphones now usually have two cameras. Let’s say the first one is on the backside to take good quality photos and the other one is on the front panel to make video calls and take selfies. Only few years back were the rare cameras in phones used to capture basic images but now, with the advent of latest algorithms and updated software solutions, high quality pictures are being produced as a result. The resultant images are no less than that captured by the DSLR (Digital Single-Lens Reflex) Camera.
Camera is one of the most advanced devices on the smartphone and adds up to its overall functionality.
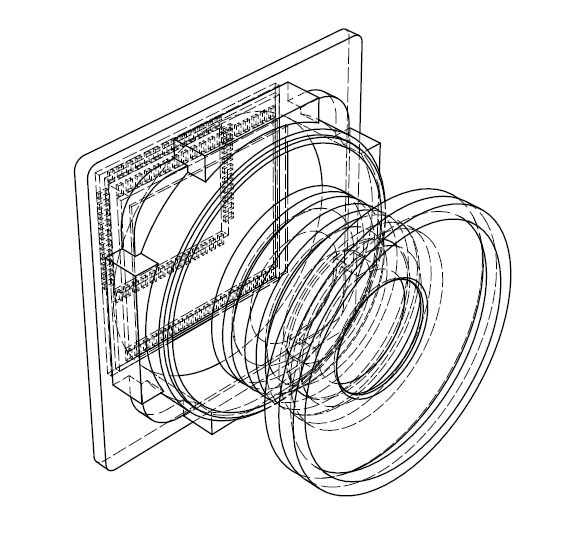
The above photograph shows the entire module of the internal camera located on the smartphone. In latest smartphones, manufacturers place up to three rear cameras, which can differ in the make and in the technology used.
 |
The glass cover is the only thing you can see on the back of your smartphone. It protects the lens inside against water and dust. Sometimes the cover is made of Corning Gorilla Glass technology tha provides protection against scratches |
 |
The lens aperture is responsible for adjusting the value of the light passing through the lens to the CMOS sensor. In digital cameras, the aperture can be adjusted manually. On the smartphone, the lens aperture has a fixed value which cannot be changed. |
 |
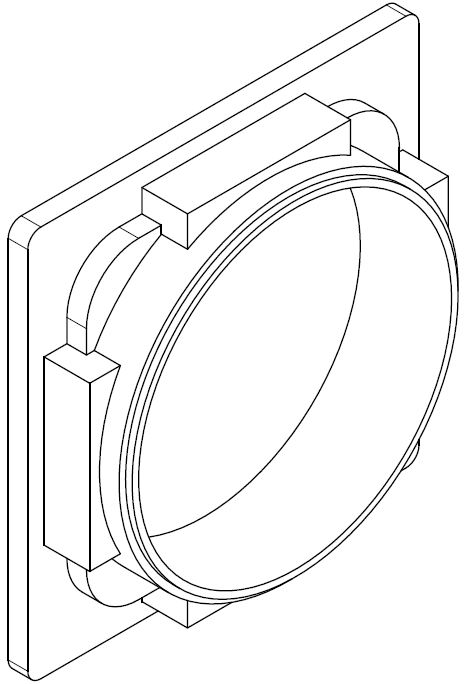
The lens is responsible for focusing the light beam on the CMOS sensor. Some of them may move a bit to focus on an interesting point (autofocus). |
 |
The CMOS sensor is responsible for detecting incoming light. Together with the Bayer filter, it is possible to recognize RGB colors. The most common parameter for a CMOS sensor is the number of MPx (megapixels). |
 |
ISP coprocessor is the last image processing point. It is usually not part of the camera system but is built into SoC. Together with an advanced program it can capture and save a picture. |
 |
The cover body is usually made of aluminum. The main idea is to connect and hold all the elements of the camera. Sometimes you can also find a gyroscope inside for optical image stabilization. |
 |
All parts together form a single camera on your smartphone. Different manufacturers can use different materials, but for now the main idea is still the same. |
MEGAPIXELS / CMOS Sensor
The main idea of creating photos using a smartphone is very similar to an ordinary digital camera. The camera on the smartphone has several parts but the most important is the active pixel sensor. This sensor is a light sensor in which each “pixel” has a photodetector and an active amplifier. The most common active pixel sensor is CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor). The most well-known parameter is the megapixel. This value shows how many individual points a CMOS sensor has.
1 Megapixel = 1 million pixels.
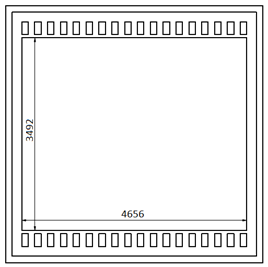
More megapixels mean better image quality because the software becomes more informed and intelligent due to the sensor. According to pic 6.2, the number of megapixels from this CMOS sensor is:
4656*3492 = 16 258 752 pixels ≈ 16 MPx
The CMOS matrix is made of millions of elements with the following structure:
- Photosensitive element, working on the principle of a photodiode digital analog amplifier
- Analog-to-digital converter
- Micro lenses, the task of which is to focus light on the photosensitive element Color filter (Bayer filter) responsible for the fact that the pixel is sensitive only to a certain spectrum of light
BAYER FILTER
The CMOS sensor is used only to recognize the value of light, and then electronic components (transistors etc.) change this value to an analog signal. When we use only a single value of light, we can save images only in grayscale. To recognize and save color photos, the Bayer filter must be used on each CMOS sensor. This filter is placed directly on the CMOS sensor and allows you to recognize three different analog values for each color (RGB, R-red, B-blue and G-green). After these calculations, these three values can be mixed together and create a color photo.

This method of light recognition is the reverse method for displaying light through modern display matrices. Liquid crystal screens emit any color by mixing and displaying three colors together at one point called a screen pixel.

More information in e-books:
APERTURE SIZE
The lens aperture is a very important element in professional photography. In the digital camera, the amount of light passing through the lens to the CMOS sensor can be adjusted. Unfortunately, this solution is not possible on the smartphone because of it being very susceptible to mechanical damage, and mechanical components can take up a lot of space inside the smartphone.
For this reason, a fixed aperture value is used, and this number can be found for each camera in the parameters of the smartphone. If you have two or three camera sensors, each of them may have a different aperture size.
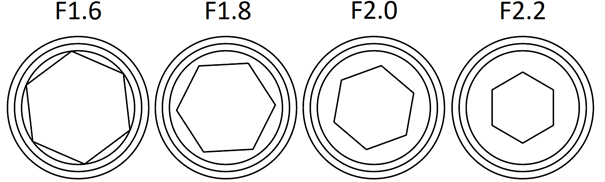
The aperture size of the lens is described by its F number, which is calculated using the lens. A larger F number means a smaller hole and less light passing through the lens into the CMOS sensor. This means that on a bright day you should use the camera with F2.0, and in dark places you should use the size of the aperture with the value F1.5.
PIXEL SIZE
The megapixel value of the sensor is not the only physical parameter that improves the quality of the images. The smaller the CMOS sensor, the worst the picture quality will be. For this reason, manufacturers of the main camera, instead of 16 megapixels, use a 12 megapixel CMOS sensor. The final image quality will be better because each individual pixel will be more sensitive and resistant to interference.
For the same physical size of the CMOS matrix, the pixel size will be larger for 12MPx (1μm for 16Mpx and 1.4μm for 12Mpx). For 16Mpx sensor and 1µm size for one pixel you can calculate how big your CMOS matrix is.
Width = 4656 pixels * 1µm = 4,656mm.
Height = 3492 pixels * 1µm = 3,492mm.
AUTOFOCUS
When you take a picture using a smartphone, you try to make a sharp image with all the edges very clear at an interesting point. For this reason, you must use the autofocus function to set the lens position at the point. Currently, manufacturers of mobile phones are trying to improve the way in which auto-focus works on a smartphone. At this point, you must know that we can separate them on the software and hardware side. On the picture below you can observe and imagine that by changing the position of the lens, you can change the focusing of light on the CMOS sensor.
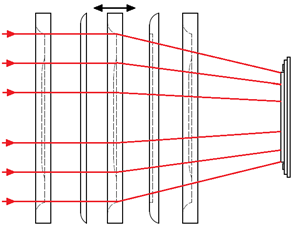
To find the best position for the lens, we can use the software’s feedback to the lens movement mechanism. Before pressing the button to take a picture, the smartphone’s software constantly performs complex calculations to find the highest contrast (first solution) or phase detection autofocus for incoming light (second option). Both of these methods are performed on the software side and require the necessary calculations in real time by the ISP coprocessor.
The best solution to adjust the position of the lenses is the hardware feedback. This is done using an infrared laser sensor located near the CMOS sensor of the main camera. In this solution, the processor calculates only the distance from the laser sensor. With this solution you can get faster response and better feedback in low light.
FLASH
This is an additional parameter in the camera’s smartphone specification, which should be checked. This is a flash lamp that is very important when you want to take pictures inside dark rooms. There are various solutions on the market, such as LED, 2xLED or with a different flash temperature, which may be white or yellow (cold or warm).
FOCAL LENGTH
This parameter is now very popular and presented in millimeters (mm). Sometimes in the smartphone’s specifications you can find information that the camera has a wide-angle lens or even an ultra-wide angle lens. This value is not a measure of the actual length of the lens. In fact, it’s the optical distance from the point where the light rays are in the form of a sharp image.
The focal length tells us about the angle of view or how much of the scene will be captured. If the focal length is larger, the picture will be narrower and closer. On the other hand, if the focal length is smaller, you will get a wider angle of view and a smaller magnification.
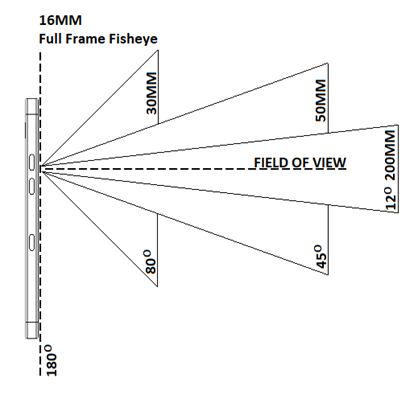
Focal values below 25 can be called wide-angle cameras. This hardware function is very useful when taking pictures of landscapes or inside small spaces. For portraits or individual items, use a standard camera with a focal length (30mm – 50mm). Wide-angle cameras can also change the disproportion of images by the fish-eye effect.
OPTICAL IMAGE STABILIZATION
Optical stabilization is also available in portable devices. Image stabilization usually supports video recording by eliminating hand shake. Manufacturers use two solutions to eliminate vibrations.
The first way is complex calculations performed by the processor. The stabilization effect depends on the additional sensors used (accelerometer and gyroscope) and on the processor’s performance. In this method, the image during recording is slightly enlarged. During image recording, the smartphone software tries to avoid fast image shake by acting inversely to the sensor force value. The image is enlarged to provide sufficient buffer space for the software and space to move and manipulate the recorded image.
The second solution is more advanced and is called optical image stabilization. In this case, the gyroscope necessary for tracking vibrations is located inside the camera module. In this case, the lens module moves slightly sideways or up and down during vibrations or rapid movement. The internal sensor provides information on vibrations directly to the camera module, which can compensate for vibrations directly affecting the camera module. This solution is very useful in dark environments and during sports video recordings.
SUMMARY
Smartphones are designed to deliver only basic data about the captured image to the software. The other effects (white balance, sensitivity, ISO etc.) are added by calculations made by the software. In latest smartphones, you can find a huge number of options that depend on the software and the ISP coprocessor performance. You can also get unprocessed photos, saved as a RAW file. In the list below you can find out all of the most important features performed by the additional software:
| Picture Software Features: |
| Manual focus, Object tracking, RAW image capture, HDR, Panorama, Face detection, Burst mode, Night mode, Exposure compensation, ISO control, White balance presets, Shutter speed control, Touch to focus, Self-timer, Digital zoom, Geotagging. |
| Video Software Features: |
| 3840×2160 (4K UHD) (60 fps), 1920×1080 (Full HD) (60 fps), 1280×720 (HD) (240 fps) High Dynamic Range mode (HDR), Time-lapse video, Digital image stabilization, Video calling, Video sharing. |







[…] Described here are the basic construction and all the necessary parameters that can be found in the specification of the smartphone. […]
Comments are closed.