When we consider the speed of a smartphone, processor is one of the most important parameters. To compare different smartphone processors, we mainly depend on software framework programs. This performance coming from frameworks is represented by score number, and depends mostly on the CPU’s working frequency and core numbers.
Couple of years ago, together with all basic calculations, CPU was responsible for image and game performance. Now these parts of calculations are covered by GPU or NPU co-processor. Sometimes CPU processor and co-processors are built in the same cover (System on a Chip – SoC). Inside the chip you can also find out a co-processorfor camera processing (ISP) and all network chipsets (LTE, 5G, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and location).
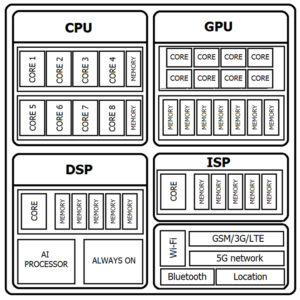
Scheme blok of Smartphone processor
The following components can be found inside the smartphone chip:
CPU – Central Processing Unit, main calculations
GPU – Graphics Processing Unit, vector and 3D calculations
DSP – Digital Signal Processor, audio signal calculations
ISP – Image Signal Processor, image signal calculations
NPU – Neural Processing Unit, artificial intelligence calculations
Memory – Space for CPU, GPU, ISP, DSP and NPU temporary calculations
Communication Systems Chip – necessary to communicate your smartphone with external world.
Central processing unit (CPU)
Basic parameter for CPU processor is working frequency represented in a Hertz [Hz] value. 1Hz means one cycle per second. For microprocessor, it means that in one second it can make one very single operation (move, add or copy). For example, multiplication of two numbers can take 3 operations, so to make it in one second, we need a processor with 3Hz. Latest smartphones have CPU with 2800MHz,which means that they are able to make 2 800 000 000 operations per second.
Another important parameter is the core number. Every processor is made of core, memory unit, registers, arithmetic co-processors and a number of buffers. Usually one core is responsible for one calculation, and the speed of this calculation can be represented by a Hertz value. If you want to make two operations, they have to be done one by one. As soon as the processor finishes one calculation, it will take care of the next one. When you have smartphone with two cores, the microprocessor, instead of making calculations one by one, can work on two tasks simultaneously. In smartphone applications it can look like one core is responsible for operating system calculations, and second for music app working in the background. The latest smartphones have from 6 to 8 cores to improve performance and user experience.
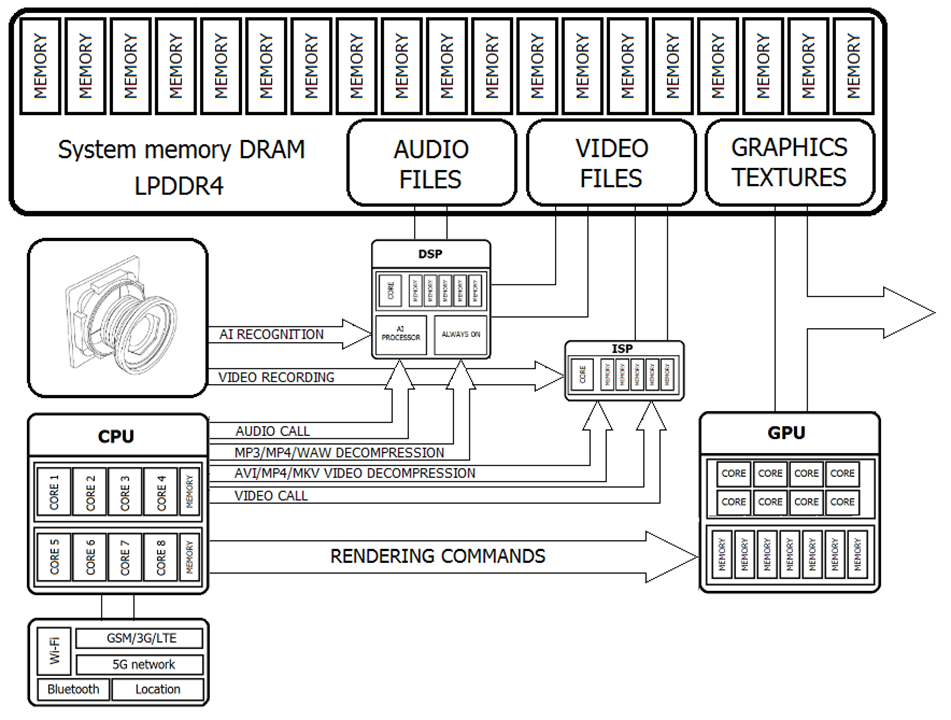
Smartphone CPU connections for complicated calculations
CPU is the main brain of your smartphone and is responsible for all calculations performed inside the operating system. Sometimes some calculations are so complicated (video, game or AI), that CPU has to use external co-processors to achieve better performance. Many manufacturers make processors with couple of cores and half of them work at a lower frequency. These slower cores are responsible for low performance calculations in background, and they can improve the lifetime of your battery.
Every processor is made in some lithography level. Latest one has 7nm lithography process. Smaller lithography level means that on the same space, it is possible to put more transistors or cores. Going down to smaller lithography level means same as going up to the next level on the technology process. Every new technology lever brings us more performance and less power consumption processors.
More information in e-books:
Graphic processing unit (GPU)
3D graphic and 2D picture calculations are so complicated that they can consume 100% of your smartphone performance. To handle this issue inside your smartphone, CPU uses additional GPU co-processor. GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is responsible for all 3D render calculations as well as for user interference displaying. To calculate one 3D scene, CPU needs thousands of calculations (add, multiply etc.).
GPU instead has some extra hardware instructions inside and due to that couple of 3D calculations can be made in one cycle. The second advantage is a greater number of core units inside GPU co-processor. This is the next reason why GPU unit makes much faster graphic calculations.
For GPU you can find out the same values like for CPU (working frequency, cores, memory, lithography level etc.). GPU has some extra software/hardware drives features (OpenGL / OpenCL / DirectX 12 / Vulkan) which helps GPU calculate graphic vectors.
Digital Signal Processor (DSP)
DSP is a specialized co-processor with architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSP is responsible mostly for measuring, filtering, compressing and decompressing continuous analog signal to digital signal. In your smartphone, this processor can be used to record sound around you and save it in the memory as a *.mp3 file. Usually DSP processors have a better power efficiency, thus they are more prone to improving your battery’s life.
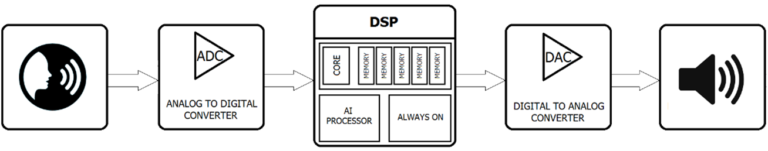
DSP processor
Inside DSP you can also find Always On Chip, which is responsible to work all the time in background. System can be used for unlocking the smartphone or work together with AI processor for voice recognition.
Image Signal Processor (ISP)
ISP is another co-processor very similar to DSP, but instead of audio signals ISP is responsible for video decoding. ISP has some specific cores and instructions for all modern video post processing effects (Autofocus, Auto exposure, Auto white balance, corrections of lens imperfections, noise reductions, filtering, HDR, cleaning and JPEG conversion). Also high speed camera (slow motion) or video resolution (1080p or 4k) depends on ISP co-processor performance.
Neural Processing Unit (NPU)
NPU (Neural Processing Unit) is also recognized as AI Processor. In smartphone, it is already used as artificial intelligence accelerating co-processor. We use this extra processor for hardware acceleration for artificial intelligence applications especially artificial neural networks, machine vision and machine learning.
Some of the applications, like recognition object on the picture, need a lot of calculations to find out what is on the picture. The speed of all these calculations can be increased by 10 times by NPU co-processors. This acceleration involves optimized memory use for lower precision arithmetic.






[…] CPU – Central processing unit […]
Comments are closed.